Raw Material Storage Compliance: Definition, Importance & Key Compliance Areas

Raw material storage compliance refers to the set of regulatory, safety, and quality standards that govern how raw materials are received, stored, handled, and monitored before production. Raw material storage compliance ensures that materials such as food ingredients, chemicals, metals, or packaging inputs remain safe, traceable, and fit for use throughout their storage lifecycle.
In everyday terms, it is similar to storing groceries at home, keeping vegetables in the refrigerator, dry grains in airtight containers, and cleaning chemicals away from food to prevent spoilage or contamination. In industrial settings, the same logic applies but with stricter controls around temperature, humidity, segregation, labeling, and shelf-life management to meet legal and quality requirements.
According to the FAO’s The State of Food and Agriculture report (2019), nearly 14% of global food loss occurs before reaching retail, with improper storage and handling being a major contributor. Similarly, the paper Impact of Poor Storage Practices on Manufacturing Quality published in the Journal of Supply Chain Management (2020) highlights that non-compliant storage conditions can increase defect rates by up to 25% in manufacturing environments.
These findings underline why key compliance areas, such as environmental controls, inventory rotation (FIFO/FEFO), contamination prevention, and documentation, are critical not only for regulatory adherence but also for cost control, product quality, and customer safety.
What Is Raw Material Storage Compliance?
Raw material storage compliance is the adherence to regulatory, safety, and quality standards that govern how raw materials are managed within a facility to ensure they remain safe, usable, and traceable before production.
It focuses on ensuring that raw materials are:
- Stored under approved environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, ventilation)
- Properly labeled for identification, traceability, and expiry tracking
- Segregated to prevent contamination or cross-mixing
- Handled using defined SOPs and safety guidelines
- Monitored and documented through regular inspections and audits
- Aligned with applicable industry regulations and quality standards
These practices help organizations maintain product quality, meet regulatory requirements, and reduce operational risks.
Why is Raw Material Storage Compliance Critical in Manufacturing?
Raw material storage compliance is critical in manufacturing because it directly affects product safety, quality, and operational reliability.
- Ensures safety, quality, and traceability by maintaining controlled storage conditions and clear identification of raw materials throughout their lifecycle
- Minimizes contamination and spoilage through proper segregation, hygiene controls, and environmental monitoring
- Supports audit readiness by aligning storage practices with regulatory, safety, and quality standards and maintaining accurate documentation
- Impacts production consistency by ensuring raw materials remain stable and fit for use, reducing defects, rework, and downtime
These factors help manufacturers maintain compliance, protect brand reputation, and achieve efficient, uninterrupted production.
Which Regulations and Standards Govern Raw Material Storage?
The regulations and standards that govern raw material storage include GMP, ICH Q9, MSIHC Rules, and ISO 22716, each addressing different aspects of storage, handling, and risk control across industries:
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices): Core quality framework that defines requirements for proper storage, handling, labeling, segregation, and status control of raw materials to prevent contamination and mix-ups.
- ICH Q9 (Quality Risk Management): Focuses on risk assessment and mitigation related to storage conditions, hold times, and material degradation, especially in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- MSIHC Rules, India (Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules): Regulate the safe storage, labeling, and handling of hazardous raw materials to minimize risks to people, property, and the environment.
- ISO 22716: GMP standard for the cosmetics industry, emphasizing controlled raw material storage, traceability, inventory status, and prevention of contamination.
These regulations altogether ensure raw materials are stored safely, remain fit for use, and comply with industry-specific legal and quality requirements.
How Should Raw Materials Be Stored to Ensure Compliance?
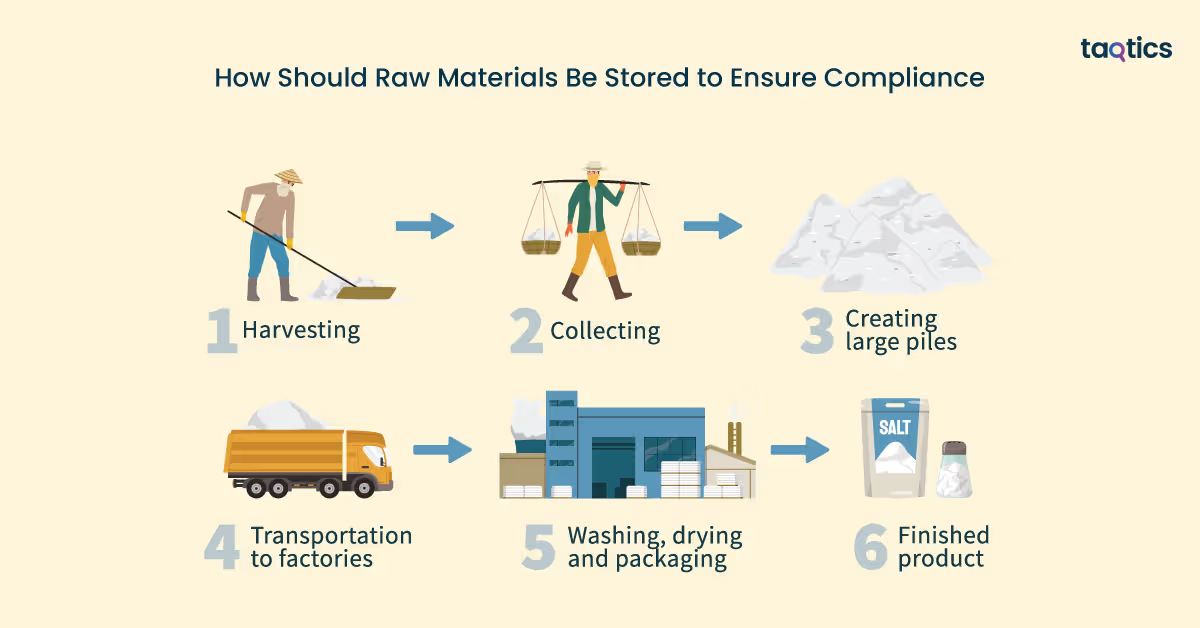
Raw materials should be stored in a structured and controlled manner to ensure compliance with regulatory, safety, and quality standards.
- Environmental control: Storage conditions should be defined based on the material’s nature, such as temperature-sensitive chemicals, hygroscopic powders, or perishable ingredients. Climate-controlled zones must maintain specified temperature and humidity ranges, supported by calibrated sensors, alarms, and routine log reviews. Deviations should trigger corrective actions and documented investigations to prevent material degradation.
- Hygiene and pest control: Storage areas must follow strict housekeeping standards to avoid contamination from dust, moisture, or pests. Raw materials should be stored off the floor (for example, a minimum of 1.5 ft) and away from walls (around 0.5 ft) to allow cleaning, inspection, and air circulation. Regular cleaning schedules, pest-control treatments, and inspection records form a critical part of compliance.
- Inventory management: Managing inventory involves two approaches, FIFO/FEFO, and Traceability.
- FIFO/FEFO: Applying First-In, First-Out or First-Expiry, First-Out ensures older or soon-to-expire materials are used first, reducing waste and preventing the use of expired stock.
- Traceability: Each material must be clearly labeled with its name, internal code, batch or lot number, receipt date, and expiry or retest date. These labels should be linked to digital or manual records that track movement, usage, and remaining quantities.
- Segregation: Materials must be physically separated based on both status (quarantine, approved, rejected, returned) and type (hazardous, flammable, allergens, sensitive materials). Clearly marked zones, color coding, and signage help prevent mix-ups and unauthorized use, especially during audits or high-volume operations.
- Safety & handling: Proper material-handling equipment, such as forklifts, pallet jacks, or cranes, should be used to avoid damage and workplace injuries. Hazardous or flammable materials must be stored in approved cabinets or containment systems with appropriate safety labels, spill kits, and emergency response instructions readily available.
- Access control: Storage areas should be accessible only to trained and authorized personnel. Entry logs, badge systems, or controlled keys help ensure accountability, while visitors must be supervised to prevent accidental contamination or mishandling.
- Documentation: Comprehensive documentation underpins compliance. This includes approved SOPs for storage and handling, training and competency records for staff, inventory and environmental logs, and deviation or discrepancy reports. Any inconsistencies, such as stock mismatches or environmental excursions, must be investigated, corrected, and formally recorded.
By implementing these detailed storage controls, manufacturers can ensure regulatory compliance, protect raw material quality, maintain audit readiness, and support consistent, safe production outcomes.
What are the Risks of Non-Compliance in Raw Material Storage?
The risks of non-compliance in raw material storage are significant and can impact manufacturers operationally, financially, and reputationally. When storage standards are not followed, even minor lapses can escalate into serious compliance and business failures. These risks can include product recalls, penalties, legal consequences, loss of certification, and damage to brand reputation.
- Product recalls and penalties: Improper storage conditions can lead to contamination, spoilage, or degradation of raw materials, resulting in unsafe finished products. Regulatory authorities may mandate recalls, impose fines, or suspend operations, leading to direct financial losses.
- Legal consequences: Non-compliance with storage regulations can violate safety, environmental, or consumer protection laws, exposing organizations to lawsuits, regulatory actions, and long-term legal liabilities.
- Loss of certification: Failure to meet standards such as GMP, ISO, or industry-specific regulations can result in suspension or withdrawal of certifications, limiting market access and affecting customer trust.
- Damage to brand reputation: Public recalls or compliance violations can erode customer confidence, harm brand credibility, and lead to loss of long-term business relationships that are difficult to rebuild.
The 2018 FDA recall of multiple pharmaceutical and food products was linked to inadequate storage and handling conditions, where temperature and hygiene lapses at supplier warehouses led to contamination risks. The incident resulted in nationwide recalls, regulatory warnings, and lasting reputational damage for the companies involved, highlighting how failures in raw material storage compliance can have far-reaching consequences beyond the factory floor.
What Tools or Software Help Ensure Raw Material Storage Compliance?
The tools and software that help ensure raw material storage compliance are designed to automate controls, improve visibility, and maintain audit readiness across storage operations.
- Inventory management systems: Enable real-time tracking of raw materials by batch, lot, and expiry date, support FIFO/FEFO practices, and improve traceability while reducing manual errors.
- Digital checklists: Standardize storage inspections, hygiene checks, and safety audits, ensuring SOPs are followed consistently and deviations are captured and addressed promptly.
- Audit-ready documentation platforms: Centralize SOPs, training records, inventory logs, and compliance evidence, making internal audits and regulatory inspections faster and more reliable.
- Environmental monitoring systems: Use automated sensors to continuously track temperature, humidity, and ventilation, with alerts for deviations to prevent material damage and non-compliance.
These tools help organizations maintain consistent compliance, reduce risk, and improve overall storage efficiency.
How Does Taqtics Simplify Raw Material Storage Compliance?

Taqtics simplifies raw material storage compliance by centralizing compliance activities into a single, easy-to-use digital platform that replaces manual checks, spreadsheets, and fragmented records. It helps manufacturers maintain consistent storage conditions, follow regulatory standards, and demonstrate audit readiness without adding operational complexity.
Taqtics is a cloud-based compliance and operations management platform designed for manufacturing environments. It digitizes SOPs, audits, and monitoring processes, enabling plant teams to track raw material storage requirements in real time while giving leadership complete visibility across warehouses and facilities.
The key features of Taqtics that can help in raw material storage compliance
- Custom compliance checklists: Taqtics allows businesses to create role-based, site-specific checklists aligned with GMP, ISO, HACCP, or internal standards. This ensures staff consistently verify storage parameters such as segregation, labeling, FIFO/FEFO, and cleanliness during daily checks.
- Real-time storage audits: Storage audits can be scheduled, assigned, and completed on mobile devices. Findings are logged instantly with timestamps, photos, and comments, reducing delays and improving accountability across storage areas.
- Temperature and humidity logs: Taqtics digitizes temperature and humidity monitoring for warehouses, cold rooms, and sensitive raw materials. Logs are automatically recorded and stored, eliminating manual entries and reducing the risk of missed or incorrect readings.
- Automated alerts and corrective actions: When storage conditions deviate from defined thresholds, Taqtics triggers instant alerts and assigns corrective actions. This enables quick intervention before raw materials are compromised or compliance violations escalate.
- Compliance dashboards and reports: Managers get real-time dashboards showing audit scores, non-conformities, and closure status. Audit-ready reports can be generated instantly, simplifying internal reviews and external regulatory inspections.
A mid-sized food ingredient manufacturer implemented Taqtics to manage raw material storage across multiple warehouses. Before adoption, audits were paper-based and temperature logs were maintained manually, leading to gaps during inspections. After deploying Taqtics, the company standardized storage checklists, automated environmental monitoring, and reduced non-compliance incidents by improving response times to alerts. As a result, audit preparation time dropped significantly, and the manufacturer achieved more consistent compliance across all storage locations.
What Temperature Should Raw Materials Be Stored At?
The temperature at which the raw materials should be stored depends on the nature of the material, its sensitivity to heat or moisture, and the regulatory standards governing the industry. In general, storage temperatures are defined to prevent spoilage, contamination, chemical degradation, or loss of functional quality.
The standard storage temperature guidelines that manufacturing units must follow revolve around four major areas.
- Dry raw materials (grains, powders, packaging materials) are typically stored at 15°C to 25°C in a cool, dry environment to avoid moisture absorption, pest activity, and quality deterioration.
- Refrigerated raw materials (perishable food ingredients, dairy inputs, certain pharmaceutical materials) should be maintained at 2°C to 8°C to control microbial growth.
- Frozen raw materials are stored at –18°C or below to preserve freshness and prevent enzymatic or microbial activity.
- Temperature-sensitive chemicals and additives usually require controlled room temperature, around 20°C to 25°C, as specified in manufacturer guidelines or Safety Data Sheets (SDS).
Regulatory frameworks such as GMP, HACCP, ISO 22000, and ISO 9001 emphasize adherence to manufacturer-recommended storage conditions and continuous monitoring. Best practices include maintaining documented temperature logs, using calibrated monitoring devices, and setting alerts for deviations to ensure raw materials remain compliant and fit for use.