Retail Store Resource Management: Overview, Types, Importance, Management Guide, Tools & Challenges

Retail store resource management is about more than just stocking shelves and serving customers. Retail store resource management requires a well-coordinated system that ensures every resource is used strategically. It helps businesses align people, products, space, and systems to meet customer demand effectively and stay profitable.
By leveraging smart resource management, retailers can achieve significant results. A study by the National Retail Federation found that retailers who optimize their resource allocation can see a 20% increase in sales and a 15% reduction in operating costs. These gains come from optimizing staff scheduling, improving stock control, and enhancing in-store experiences.
This guide dives into every essential aspect of managing resources in a retail environment, from understanding different resource types like staffing, inventory, and data, to learning why efficient management drives customer satisfaction and profitability. It also explores actionable steps like forecasting, scheduling, and utilization, and highlights how digital tools like Taqtics simplify and scale these processes.
Whether you’re managing a single location or a nationwide chain, effective resource management is what turns good retail into great retail, creating smoother operations, better decisions, and happier customers.
What is Retail Resource Management?
Retail Resource Management (RRM) refers to the strategic planning and efficient utilization of a retailer’s resources, such as labor, inventory, store space, and technology, to optimize performance and improve customer satisfaction. Retail resource management ensures the right resources are available at the right time and place to meet consumer demand effectively.
While in workforce management, RRM involves forecasting customer foot traffic to schedule the optimal number of staff during peak shopping hours, it ensures shelves are stocked with in-demand products, reducing overstock and stockouts in inventory management. RRM also includes managing fixtures, digital tools, and store layouts to enhance the shopping experience and drive sales.
For example, a clothing retailer uses RRM software to track sales data, predicting which items will be popular in the coming season. Based on this, they allocate more shelf space to those items and adjust employee shifts to handle expected crowds. This prevents overstaffing during slow times and ensures popular products are always available, enhancing both profitability and customer satisfaction.
RRM aligns all retail operations to work smarter, not harder, supporting seamless customer experiences and efficient business performance.
What are Types of Resources in Retail Stores?
The types of resources in retail stores are staffing, inventory, finance, store layout, marketing, data management, and customer service.
Staffing
Employees are the backbone of retail operations. They include the sales associates, managers, stock handlers, and cashiers. Proper retail staffing optimization ensures that there are enough team members to assist customers, manage inventory, and maintain store cleanliness. Scheduling staff based on foot traffic and peak hours enhances productivity and service quality.
Inventory
Inventory includes all the products available for sale. Effective inventory management ensures that popular items are always in stock, while excess or outdated items are minimized. Using inventory management software is great as it makes the process smooth, helps reduce storage costs, and avoids lost sales due to stockouts.
Finance
Financial resources are necessary for running daily operations—purchasing inventory, paying staff, covering utilities, and investing in marketing or store improvements. Sound financial planning and budgeting are essential to maintain profitability and sustainability.
Store Layout
The physical arrangement of the store impacts customer flow and sales. A well-organized layout guides shoppers efficiently through the store, highlights key products, and creates a pleasant shopping environment. This includes shelving, signage, product placement, and checkout areas.
Marketing
Marketing involves promoting the store and its products to attract customers. This can include advertising, in-store promotions, social media, and loyalty programs. Effective retail marketing and advertising strategies help drive traffic, build brand awareness, and increase sales.
Data Management
Data from sales, customer behavior, and market trends is valuable for decision-making. Retailers use data to forecast demand, personalize marketing, manage inventory, and improve overall efficiency. Data-driven retail store operations improve productivity and boost profitability.
Customer Service
Excellent customer service techniques build trust and loyalty. This includes answering inquiries, handling returns, and resolving complaints. Friendly, knowledgeable staff and clear service policies enhance the customer experience.
These resources collectively form the foundation of a successful retail operation.
Why is Store Resource Management Important?
Store resource management is important for the smooth functioning and long-term success of any retail business. It involves effectively planning, organizing, and utilizing resources such as staff, inventory, finances, space, and technology.
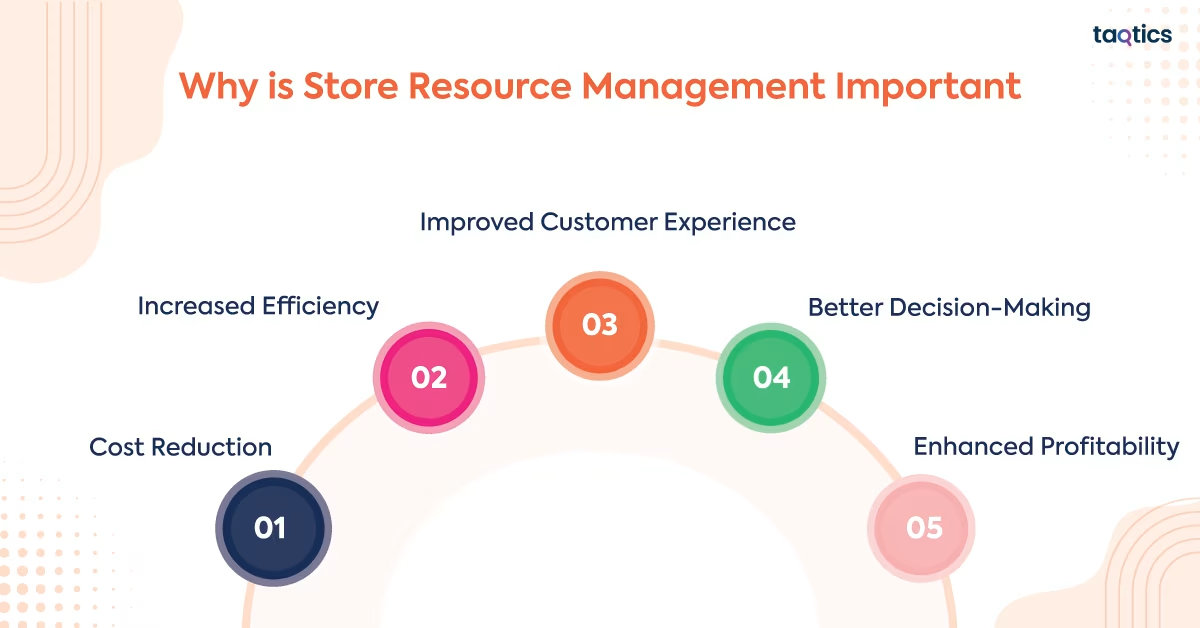
Cost Reduction
Proper resource management helps retailers control unnecessary expenses. By optimizing staffing levels, avoiding overstocking, and reducing waste, retailers can significantly lower operational costs. For example, using sales data to adjust inventory purchases prevents tying up money in unsold products.
Increased Efficiency
When resources are managed well, daily operations run more smoothly. Staff are scheduled based on store traffic, shelves are stocked with the right products, and checkout systems are streamlined. This reduces delays, minimizes errors, and increases productivity across departments.
Improved Customer Experience
A well-managed store ensures that customers find what they need quickly, receive assistance promptly, and enjoy a clean, organized shopping environment. Staff availability, product accessibility, and fast checkouts all contribute to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Better Decision-Making
Resource management relies heavily on data, such as sales trends and customer behavior. This information supports informed decision-making in areas like purchasing, promotions, and staffing. Data-driven decisions help stores adapt quickly to market changes and customer needs.
Enhanced Profitability
Ultimately, effective resource management leads to higher profitability. Lower costs, efficient operations, and happier customers drive increased sales and repeat business. By aligning resources with store goals and customer demand, retailers can maximize return on investment.
Store resource management is not confined to managing supplies or schedules, but also creating a balanced, responsive retail environment that supports growth, profitability, and a positive customer experience.
How to Manage Retail Store Resources?
To manage retail store resources effectively, businesses must follow six steps, which include resource planning, resource allocation, resource scheduling, resource leveling, resource smoothing, and resource utilization.
1. Resource Forecasting
This involves predicting future resource needs based on historical data, trends, and expected demand. You can use sales data, seasonal trends, and promotional calendars to estimate staffing, inventory, and financial needs.
For example, if holiday sales are expected to increase by 20%, plan to hire temporary staff and stock up accordingly. Accurate forecasting prevents over- or under-preparing.
2. Resource Allocation
It is about distributing resources to different areas of the store based on priority and demand.
Businesses can assign more staff to high-traffic departments and allocate prime shelf space to best-selling products. Using store layout and sales data to determine where resources like labor and inventory will have the most impact.
3. Resource Scheduling
Scheduling resources involves planning when and where each resource is used, particularly staff. You can use foot traffic patterns and POS data to create efficient work schedules. Scheduling more staff during weekends or promotional events is highly recommended. For inventory, schedule restocking during low-traffic hours to avoid disrupting customers.
4. Resource Leveling
It involves adjusting the use of resources to prevent overuse or burnout, especially with labor.
You can rotate employees between tasks to balance workloads and avoid over-scheduling. If multiple tasks require the same staff, prioritize based on urgency or reassign tasks to maintain balance.
5. Resource Smoothing
Resource smoothing ensures consistent resource usage by spreading demand more evenly.
Plan promotions during traditionally slow periods to balance customer flow. Adjust staff breaks or duties to maintain consistent service levels without spikes or drops in performance.
6. Resource Utilization
It is about measuring how effectively resources are used. Track KPIs like sales per employee or inventory turnover rates. Analyze the data to identify underused or overused resources and make improvements accordingly.
By mastering these six aspects of resource management, retail stores can operate more efficiently, reduce costs, enhance customer service, and improve profitability.
What Tools can Help Manage Store Resources?
Taqtics is one of the tools that can help manage store resources. Managing store resources efficiently is crucial for maintaining operational consistency and enhancing customer experience. Tools like Taqtics offer comprehensive solutions tailored for retail and restaurant operations.
- Taqtics provides a unified platform that digitizes standard operating procedures (SOPs), enabling businesses to create, schedule, and assign tasks and checklists. Features such as geo-fencing, live photo attachments, and multi-lingual support ensure compliance and streamline daily operations.
- The platform also facilitates store audits with customizable scoring, automated action points, and real-time dashboards, allowing for prompt issue resolution and performance monitoring.
- Taqtics offers asset management tools that track equipment lifecycles, manage license renewals, and provide barcode integration for efficient monitoring.
- Designed for scalability, Taqtics supports multi-store and multi-region setups, providing real-time insights and analytics to optimize resource allocation and enhance team productivity.
Taqtics stands out as an influential tool in store resource management, offering a comprehensive suite of features that streamline operations, ensure compliance, and drive performance improvements.
What are Challenges in Retail Resource Management?
The challenges in retail resource management include inventory inaccuracy, staffing shortages, lack of standardized processes, ineffective communication, asset mismanagement, lack of real-time insights, and difficulty in scaling operations.
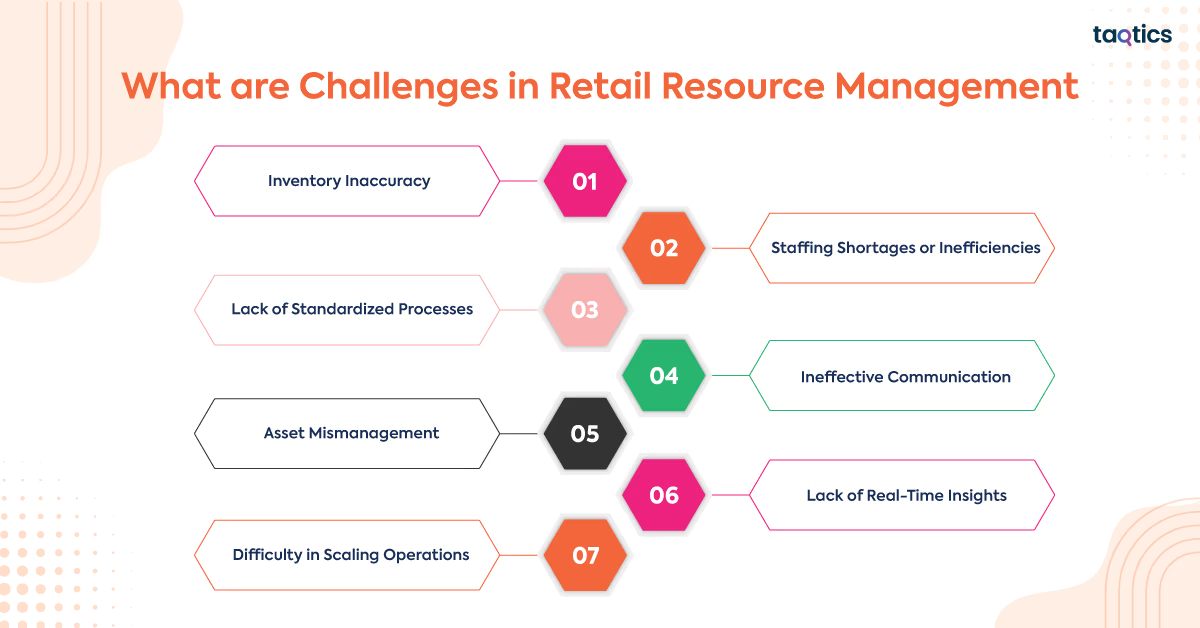
Inventory Inaccuracy
Stock miscounts lead to overstocking or stockouts, affecting sales and customer trust.
Implementing real-time inventory tracking systems with barcode scanning and automated restocking alerts can resolve the issue.
Staffing Shortages or Inefficiencies
Poor scheduling or inadequate staffing impacts customer service and sales. Using workforce management tools that analyze peak hours and forecast staffing needs accurately can be used.
Lack of Standardized Processes
Inconsistent store operations reduce efficiency and brand consistency. Digital SOP platforms like Taqtics can help standardize tasks and processes across locations, ensuring compliance and quality.
Ineffective Communication
Miscommunication between teams leads to missed tasks and poor execution. Adopt centralized communication tools that offer real-time updates, task assignments, and mobile notifications.
Asset Mismanagement
Tracking equipment, licenses, and warranties across locations is time-consuming. Use asset management software with lifecycle tracking, QR/barcode integration, and renewal reminders.
Lack of Real-Time Insights
Without timely data, decision-making is reactive rather than proactive. Leverage analytics dashboards that offer real-time KPIs on store performance, audits, and resource usage.
Difficulty in Scaling Operations
Managing multiple locations consistently becomes complex as businesses grow. Use scalable platforms like Taqtics that support multi-store management with unified dashboards and audit tools.
Addressing these challenges with the right digital tools not only streamlines operations but also boosts productivity and profitability across retail operations.